声明:本文使用JDK1.8,如果有错希望指出
在Java面试的时候,HashMap 和 Hashtable 经常被问,就想仔细分析下两者。
Java集合框架 —— HashMap
HashMap 和 Hashtable 的区别
HashMap 和 Hashtable 都是实现 Map 接口,两者主要的区别是线程安全性,同步,以及速度。
| HashMap |
Hashtable |
| 键值接受null |
键值对不能为null |
| 非synchronized |
Hashtable是synchronized,线程安全 |
| 单线程下HashMap的速度比Hashtable快 |
sychronized意味着在一次仅有一个线程能够更改Hashtable |
| 迭代器(Iterator)是fail-fast迭代器 |
Hashtable的enumerator迭代器不是fail-fast的 |
因此仅在需要线程安全的时候使用Hashtable,而如果Java5以上,还是使用 ConcurrentHashMap。
Java并发容器 ——— ConcurrentHashMap。
源码分析
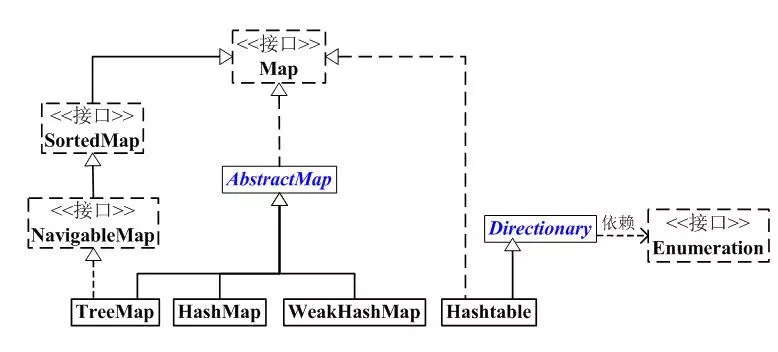
Hashtable 虽然不是继承于 AbstractMap,但它继承于 Dictionary(Dictionary 也是键值对的接口),而且也实现Map接口;因此,Hashtable 的内容也是“键值对,也不保证次序”。但和 HashMap 相比,Hashtable 是线程安全的,而且它支持通过 Enumeration 去遍历。Hashtable 采用的是数组+链表实现。Hashtable 通过 synchronized 保证其的线程安全。
数据结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| public class Hashtable<K,V>
extends Dictionary<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {
private transient Entry<?,?>[] table;
private transient int count;
private int threshold;
private float loadFactor;
private transient int modCount = 0;
private static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
protected Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Entry<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
|
初始化构造
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| public Hashtable(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Load: "+loadFactor);
if (initialCapacity==0)
initialCapacity = 1;
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
table = new Entry<?,?>[initialCapacity];
threshold = (int)Math.min(initialCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);
}
public Hashtable(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0.75f);
}
public Hashtable() {
this(11, 0.75f);
}
|
put() 操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) {
if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {
V old = entry.value;
entry.value = value;
return old;
}
}
addEntry(hash, key, value, index);
return null;
}
private void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int index) {
modCount++;
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
if (count >= threshold) {
rehash();
tab = table;
hash = key.hashCode();
index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>) tab[index];
tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
count++;
}
|
扩容 rehash()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| protected void rehash() {
int oldCapacity = table.length;
Entry<?,?>[] oldMap = table;
int newCapacity = (oldCapacity << 1) + 1;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) {
if (oldCapacity == MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)
return;
newCapacity = MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
Entry<?,?>[] newMap = new Entry<?,?>[newCapacity];
modCount++;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);
table = newMap;
for (int i = oldCapacity ; i-- > 0 ;) {
for (Entry<K,V> old = (Entry<K,V>)oldMap[i] ; old != null ; ) {
Entry<K,V> e = old;
old = old.next;
int index = (e.hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % newCapacity;
e.next = (Entry<K,V>)newMap[index];
newMap[index] = e;
}
}
}
|
get() 操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public synchronized V get(Object key) {
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
return (V)e.value;
}
}
return null;
}
|


