声明:如果本文有错误,希望指出。
ReentrantLock 位于 java.util.concurrent.locks 包下,它实现了 Lock 接口和 Serializable 接口。
ReentrantLock 默认非公平,但可实现公平的(构造器传true),悲观,独享,互斥,可重入,重量级锁。ReentrantLock 就是一个普通的类,它是基于 AQS(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer)来实现的。
ReetrantLock 基本用法
构造方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public ReentrantLock() {
sync = new NonfairSync();
}
public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();
}
|
ReentrantLock 提供公平锁和非公平锁的构造方法,默认构造方法是非公平锁。
NonfairSync 和 FairSync 都是 ReentrantLock 的内部类,继承 Sync 类。
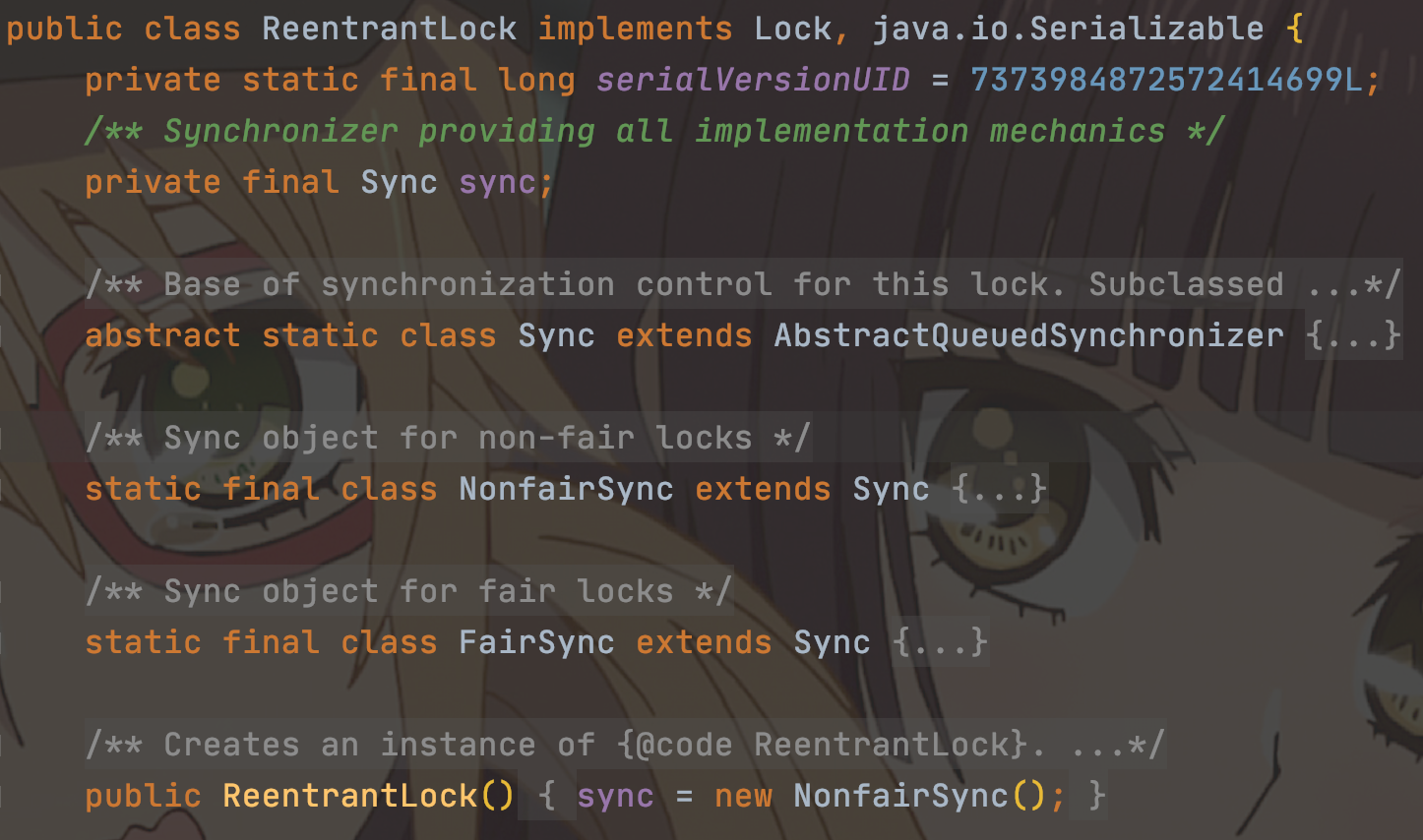
关于公平锁和非公平锁的区别,主要是在多线程情况下,获取锁的机会是否相同。
几种获取锁的方法
获取 ReentrantLock 的几种方式:
- lock(): 如果获取了锁立即返回,如果别的线程持有锁,当前线程则一直处于休眠状态,直到获取锁
- tryLock():如果获取了锁立即返回true,如果别的线程正持有锁,立即返回false
- tryLock(long timeout,TimeUnit unit):如果获取了锁定立即返回true,如果别的线程正持有锁,会等待参数给定的时间,在等待的过程中,如果获取了锁定,就返回true,如果等待超时,返回false;
- lockInterruptibly():如果获取了锁定立即返回,如果没有获取锁,当前线程处于休眠状态,直到获取锁定,或者当前线程被别的线程中断
公平锁加锁的流程(lock)
在我们使用lock的时候,由于 FairSync 继承 Sync,并重新实现了lock()方法,在源码中:
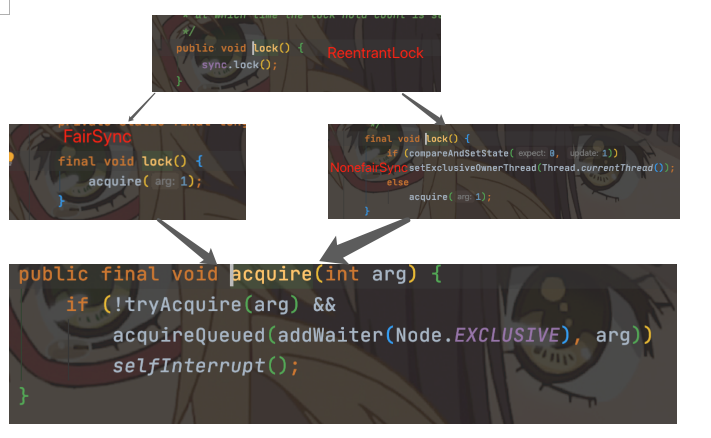
从上面的加锁流程,可以看出,不管是公平锁,还是非公平锁,最后都调用了 acquire(int arg) 方法。acquire() 方法是 AQS 中的方法,下面来看下acquire的主要流程
tryAcquire(int arg)
AQS 中的 tryAcquire 方法,具体实现交给了 FairSync 实现,这一步主要是尝试获取锁。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
public final boolean hasQueuedPredecessors() {
Node t = tail;
Node h = head;
Node s;
return h != t &&
((s = h.next) == null || s.thread != Thread.currentThread());
}
|
其中的 getState() 是获取AQS 中的state值,这个值是volatile关键字修饰的,这个字段是一个同步锁的状态,框架通过 CAS 来原子操作这个值的变化。
利用hasQueuedPredecessors()方法来判断队列中是否有其他线程,如果有,则不会尝试获取锁。如果没有,利用CAS将AQS中的state修改为1,也就是获取锁,并将当前线程设置为获取锁的独占线程。
如果state>0了,表示锁已经被获取了,这时就需要判断获取锁的线程是否为当前线程,是的话,state+1。
tryAcquire()会查看同步状态是否获取成功,如果成功,返回true,结束返回,如果!tryAcquire()==false,则调用addWaiter()方法。
addWaiter(Node mode)
如果前面的tryAcquire(int acquires)方法获取锁失败,则需要 addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE)将当前线程写入AQS队列中。
将当前线程和Node节点进行封装,AQS中节点类型有两种:SHARED 和 EXCLUSIVE,前者是共享模式,后者是独占模式。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
enq(node);
return node;
}
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) {
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
|
acquireQueued()
写入队列后,需要将当前线程挂起,利用 acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null;
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)
return true;
if (ws > 0) {
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
LockSupport.park(this);
return Thread.interrupted();
}
|
首先会进行无限循环中,循环中每次都会判断给定当前节点的前置节点,如果没有前置节点会直接抛出空指针异常,直到返回 true。
首先判断当前节点的前置节点是否是头结点,并尝试获取独占锁,如果成功,则将头结点指向当前节点,然后释放前置节点。如果没成功,则进入下一个判断条件。
根据上一个节点的 waitStatus 状态来处理 shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire()。waitStatus 用于记录当前节点的状态,如节点取消、节点等待等。
shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire() 循环尝试修改 compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL)。parkAndCheckInterrupt 该方法的关键是会调用 LookSupport.park 方法,该方法是用来阻塞当前线程。
selfInterrupt()
中断当前线程
1
2
3
| static void selfInterrupt() {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
|
非公平锁加锁模式
非公平锁的的加锁步骤和公平锁大致相同,只有两处不同(不同点在代码中标注),一处是在尝试获取锁前,直接通过CAS设置同步状态,如果成功,就将当前线程设置为偏向锁的线程;另外一处是在tryAcquire获取失败后,不需要去执行hasQueuedPredecessors方法,判断等待队列中是否还有等待线程。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| final void lock() {
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
acquire(1);
}
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
|
释放锁
公平锁和非公平锁的释放流程是一样的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;
}
|
首先会判断当前线程是否为获得锁的线程,由于是重入锁所以需要将 state 减到 0 才认为完全释放锁。
释放之后需要调用 unparkSuccessor(h) 来唤醒被挂起的线程。



